Data is currently a huge topic in this business world, and everyone would like to talk about their insights and the value they can derive from the data. There is a good reason for this — data is one of the most precious tools that marketers, agencies, publishers, media firms, and more do seem to have today.
However, data is helpful only if the quality is excellent. At best, wrong data is irrelevant, leading firms to make costly mistakes in the worst-case scenario. IBM estimates the cost to the US economy of bad data to be $3.1 trillion annually. These costs originate when personnel needs to spend on rectifying wrong data and inaccuracies causing errors with customers.
Of course, it is a tremendous chance to improve the quality of your data. One of the key tasks of data analysts is to ensure the quality of data. Data problems can be caused by errors, system modifications, software errors, or incorrect data integration/migration in the data entered by the employee or customer. Take the world’s most outstanding instructors and universities’ Data Analytics courses. Let’s examine more closely the quality of the data and why.
Data Quality Management – What is it?
Data quality is the state closely linked to its ability (or inability) to solve company tasks. Data quality management (DQM) is a set of procedures for maintaining high-quality information by a data manager or organization. These procedures are carried out during the whole data process; the acquisition, execution, distribution, and analysis.
Why does data quality matter?
Poor quality of data may cost a company $9.7 million a year. Problems with data quality result in a 20% loss in employee productivity and explain why 40% of enterprise projects fail to reach set objectives. Inaccurate data can hurt the reputation, misdirect resources, slow down information retrieval and lead to missed opportunities and incorrect insights.
Why do we need data quality management?
Data quality management is a crucial step to help you understand your data, ultimately.
Firstly, strong data quality management for all business initiatives builds the foundation. Outdated or non-trustworthy data may lead to errors and inaccuracies. A data quality management program sets a framework for the organization’s departments which lays down and implements data quality rules.
Secondly, reliable and up-to-date data provide an overview of daily activities for your firm so that you are confident that it will use all of this data in upstream and downstream applications. Data quality management also reduces overhead costs, and poor quality can result in expensive errors and supervision, such as loss of order or expenditure. Data quality management provides a basis for understanding your organization and expenses by thoroughly understanding your data.
Finally, to achieve compliance and risk objectives, you require data quality management. Good data management requires clear communication procedures and good underlying data, and data quality is a vital part of developing a data governance strategy.
Data Quality Management – Its features
A good DQM uses a system with several elements to improve the reliability of organizational data. Let us describe the different characteristics of a good DQM.
The cleansing of data corrects unknown types of data, duplicate records, and substandard data representations. Data cleansing guarantees that data standardization requirements are followed to allow analysis and insights into your data sets. The process of data cleansing also develops hierarchies and adapts data to the unique data requirements of an organization.
Data profiling is the data monitoring and cleansing process. Profiling of data is employed;
- Creates a data relationship
- Validation of accessible information with standard statistical measures
- Verification of available data with the corresponding descriptions
The technique of data profiling identifies trends that help identify, understand and expose data incompatibilities for corrections and modifications.
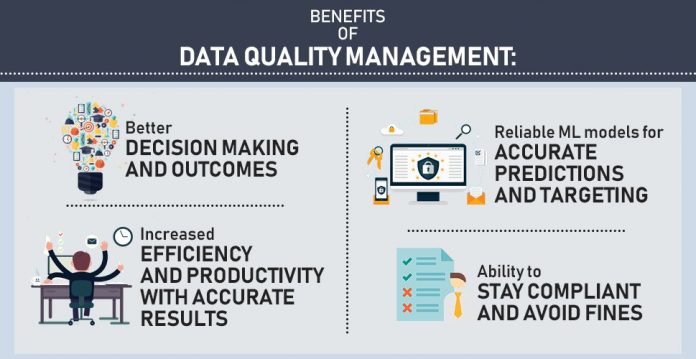
Benefits of good data quality
From a financial point of view, maintaining excellent data quality enables enterprises to lower their system costs and rectify incorrect data. Companies can also avoid operational errors and breakdowns in company processes that raise operating costs and decrease revenue.
Furthermore, strong data quality increases the accuracy of analytical applications, enabling better business decisions that raise sales, improve internal procedures and provide businesses with a competitive edge over competitors. High-quality data can assist broaden the usage of BI dashboards and analytics tools. Effective data quality management also frees data management teams from cleaning up data sets to focus on production duties.
Duties of Data quality analyst
The roles of the data analyst may differ. The specialist can fulfill the obligations of a data consumer, including the definition and documentation of the data standard, maintain data quality before being placed into the data warehouse, generally the work of the data custodian. Responsibilities of the data quality analyst can include:
- The quality control and verification of data entered by users into enterprise systems, data extracted, transformed, and loaded into data warehouses.
- Identifies and resolves the root cause of data problems
- Measurement and reporting to management of data quality evaluation results and continuous data quality improvement
- Service levels agreements, protocols for communication with data suppliers, and policy and processes on data quality assurance.
- Document the ROI for initiatives on data quality.
The companies may demand that the data quality analyst organize and provide training for staff on data quality and recommend measures to improve the data fit. The expert may also ensure that the data privacy policy of the company is obeyed.
It is up to you to assign tasks within the data quality team. However, each team must contain the person responsible for the entire process, which conducts quality checks, administers data quality standards, produces data models, and a techie who maintains data flow and stores throughout the company.
Final words
There is a change in the data analysis, and you must adjust the standards for data quality. Governments increasingly regulate data to guarantee ethics and privacy through legislation like the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation. The challenges for poor data quality are increased with natural language processing, machine learning, and artificial intelligence. It is essential to understand what comprises good data, whether you pursue a profession as a data analyst, data scientist, business analyst, or data engineer.